If you are exploring an energy storage system (ESS) for your home or business, you will quickly encounter a technical fork in the road: should you choose an AC-coupled or a DC-coupled ESS?
In this guide, we will break down the architectures, compare the pros and cons, and help you decide which setup is right for your energy needs.
What Is AC-Coupled ESS?
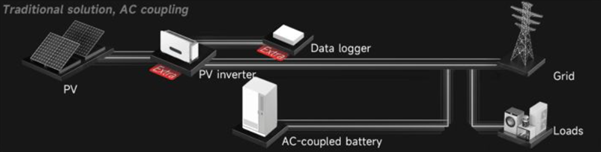
In an AC-coupled setup, the solar array and the battery storage system operate somewhat independently, connected by the main AC electrical panel of the building.
Here is how the power flows in an AC-coupled system: 1.Solar Generation: Your PV panels generate DC electricity. 2.First Inversion: A standard solar inverter converts this DC electricity into AC electricity to power your home’s appliances or feed into the grid. 3.Second Inversion: To store excess energy, a separate battery inverter (or multi-mode inverter) takes that AC electricity and converts it back into DC to charge the battery. 4.Discharge: When you need to use the stored energy at night, the battery inverter converts the DC power back into AC power.
Key Characteristic: The “double conversion” (DC to AC to DC) is the hallmark of AC coupling. It allows the solar system and the storage system to be installed at different times or even in different locations, offering significant installation flexibility.
What Is DC-Coupled ESS?
In a DC-coupled architecture, the solar panels and the battery share a single brain, i.e., the hybrid inverter.
Here is the streamlined power flow in a DC-coupled system: 1.Solar Generation: PV panels generate DC electricity. 2.Direct Charging: This DC power flows into a charge controller or hybrid inverter, which feeds it directly into the battery. 3.One-Time Inversion: The inverter converts the DC power (from either the panels or the battery) into AC only when your home needs to use it or when exporting to the grid.
Key Characteristic: Electricity stays in DC form from generation through storage and is converted to AC just once when it’s finally used. This minimizes conversion losses.

AC Coupling vs DC Coupling: What Are the Differences?
The main differences between AC coupling and DC coupling lie in three segments:
1.Efficiency DC Coupling: Because the energy flows directly from the solar panels to the battery without being inverted to AC first, DC-coupled systems are inherently more efficient. AC Coupling: The electricity may need to go through three conversion steps (PV to Grid, Grid to Battery, Battery to Load) before it is used. This results in lowered energy efficiency.
2.Cost and Equipment DC Coupling: A DC-coupled system is usually more cost-effective for new installs because it requires fewer components. You generally only need a hybrid inverter to manage both the PV array and the battery. AC Coupling: This setup requires two separate inverters: the solar inverter (which you might already have) and a new battery inverter. It typically means a higher upfront hardware cost.
3.Flexibility and Scalability AC Coupling: This architecture offers superior flexibility and scalability. You can easily add more AC-coupled batteries or expand your energy storage capacity without replacing your existing solar equipment. DC Coupling: Its scalability is generally more restricted compared to AC coupling. Since the solar panels and battery rely on a single hybrid inverter, the system’s capacity is limited by that inverter’s power rating. When to Choose Each Configuration?
So, which configuration is right for your battery energy storage system?
In short, choose DC coupling if your project prioritizes higher efficiency, lower upfront cost, and tight integration between solar and storage. This architecture is cheaper, more efficient, and easier to monitor since everything runs through one hybrid inverter.
If you are happy with your current solar inverter and just want to add backup power, choose AC coupling. It essentially “snaps on” to your existing electrical panel. It is also suitable for projects with complex site limitations since the battery can be placed far away from the solar inverter. About HYXI
At HYXI, we provide both AC- and DC-coupled ESS solutions that match different project requirements. We have over 100 core intellectual properties and more than 400 certifications from globally recognized institutions such as TÜV Rheinland, CSA, Bureau Veritas, and SGS. With 12 Global Technical Assistance Centers (GTACs) across six continents, we collaborate with international partners to promote a greener, low-carbon, and sustainable future.
Contact us today if you’re looking for a reliable solar energy battery storage solution.